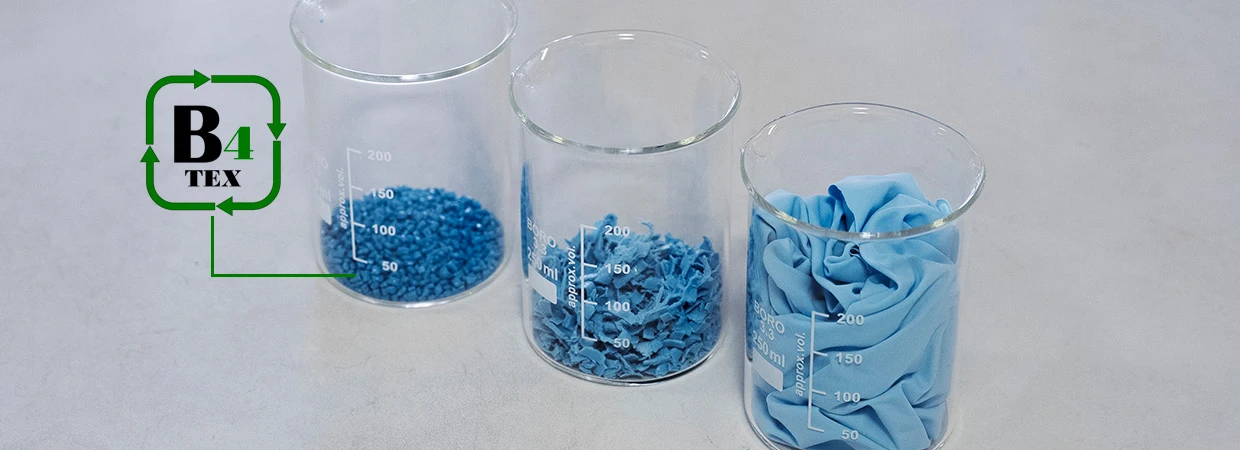
B4TEX pellets are a compound obtained from regenerated post-consumer synthetic textile fibers.
B4TEX TEXTILE WASTE RECOVERY
From textile waste to plastic pellets: SPINPET research for valorizing fashion waste


Textile waste: from waste to a resource for the furniture sector with B4TEX
How to convert post-consumer synthetic fibers into high-performance plastic materials suitable for injection molding
A real (and growing) problem.
The textile industry generates 58 million tons per year of plastic waste, accounts for 10% of global CO₂ emissions and 20% of industrial wastewater.
Yet, only 1% of garments are effectively recycled. Most end up in landfills or incinerators, also due to technological limitations, sorting difficulties and low compatibility among mixed materials (synthetic, natural and elastomeric fibers).

The objective:
adding value to synthetic textile waste
SPINPET has developed and patented a technology to recycle 100% synthetic post-consumer garments, converting them into tailor-formulated pellets suitable for injection molding.
This work has resulted in:

Two peer-reviewed scientific publications

One European patent (EP4494833A1)
The creation of the B4TEX trademark for recycled textile-based pellets
Technical challenges:
blending, degradation and microplastics.
Textile waste is extremely heterogeneous. Many garments are made of complex blends (e.g. PET + cotton + elastane), making conventional recycling difficult.
The main technical challenges include:
- thermal degradation and viscosity reduction;
- incompatibility between polymers;
- formation of microfibers during reprocessing;
- discontinuous feeding in processing equipment.
The SPINPET solution:
densification, compatibilization and formulation
SPINPET has developed a patented process that converts post-consumer garments into rigid, higher-density flakes, suitable for direct extrusion, without the need for preliminary grinding and without the risk of thermal degradation.
This ensures process continuity and significantly reduces intermediate steps, with clear advantages in terms of efficiency and material quality.

Compatibilization of polymer blends
For mixed textiles, specific compatibilizers were developed to improve interaction between PET and incompatible materials (polyamides, elastane, cellulosic fibers), optimizing melt cohesion and compound stability.

The results:
a new tunable material
Within a circular transition perspective, recycling synthetic polymers from textiles represents a concrete and scalable alternative to virgin materials, complementary to the development of biopolymers.

The resulting pellets can be used in rigid packaging, technical items, furniture components or non-structural automotive applications.

Recycled content can be modulated according to required performance.
Mechanical and rheological properties can be customized through tailored formulation.


